What is Naphtha Unit ?
Naphtha is a term used to describe a range of flammable liquid hydrocarbon mixtures that are typically used as feedstock in the production of chemicals, fuels, and solvents. In the petroleum refining industry, naphtha is a key intermediate product that is derived from crude oil and is used as a raw material in the production of gasoline, petrochemicals, and other products.
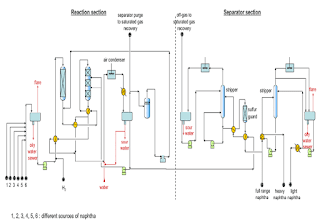
The naphtha unit in a petroleum refinery is responsible for processing crude oil and separating it into various components, including naphtha. The naphtha unit is a critical component of the refinery's operations, as it produces a feedstock that is used in the production of high-value products.
The naphtha unit process involves several steps, including distillation, cracking, and reforming. The distillation process involves heating the crude oil to vaporize the components, which are then condensed and collected based on their boiling points. In the case of naphtha, it typically boils at a temperature range of 30-200 degrees Celsius.
Once the naphtha has been separated from the other components, it is typically subjected to further processing to increase its value. One common process used to upgrade naphtha is cracking, which involves breaking down larger hydrocarbon molecules into smaller ones. This can be done through thermal cracking, where the naphtha is heated to high temperatures and then rapidly cooled, or through catalytic cracking, where the naphtha is reacted with a catalyst to promote the desired chemical reactions.
Another common process used to upgrade naphtha is reforming, which involves changing the molecular structure of the hydrocarbons in the naphtha to produce higher-octane gasoline components. This is achieved by subjecting the naphtha to heat and pressure in the presence of a catalyst.
The output of the naphtha unit can vary depending on the specific needs of the refinery and the market demand for various products. Some naphtha may be sold directly as a fuel or solvent, while other naphtha may be further processed to produce gasoline, diesel fuel, or other high-value products.
In addition to its use in the production of fuels and chemicals, naphtha is also used as a feedstock in the production of plastics, resins, and synthetic fibers. It is a versatile and important raw material that plays a critical role in the global economy.
However, naphtha is also a highly flammable and volatile substance that requires careful handling and storage to minimize the risk of accidents or spills. Refineries and other facilities that handle naphtha are subject to strict safety regulations and must take extensive precautions to ensure the safety of their workers and the surrounding community.
In conclusion, the naphtha unit is an essential component of a petroleum refinery that plays a critical role in the production of a wide range of products. The naphtha unit process involves several steps, including distillation, cracking, and reforming, and produces a feedstock that is used in the production of high-value products such as gasoline, chemicals, and plastics. While naphtha is a highly valuable raw material, it is also a highly flammable and volatile substance that requires careful handling and storage to ensure the safety of workers and the surrounding community.




Comments
Post a Comment